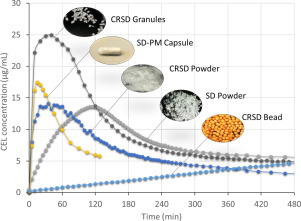
The amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) technique has been employed to formulate poorly-soluble drugs, however, development of solid dosage forms with ASD is challenging due to the high propensity of amorphous drug to precipitate upon dissolution. Thus this work aimed to explore the potential of controlled release amorphous solid dispersion (CRASD) systems using polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) as a release-retarding excipient to mitigate the drug precipitation during dissolution of poorly water-soluble drugs. A number of solid oral CRASD dosage forms in different shapes and structures were prepared to contain spray-dried SD powders of a model BCS Class II drug, celecoxib (CEL), polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) which was incorporated in varying ways. In vitro dissolution tests were performed to investigate the effect of dosage form design on the dissolution/recrystallization profiles. The results indicated that despite nearly identical formulation compositions, the dissolution/recrystallization profiles could be tailored by changing the dosage form design. Matrix-form granules demonstrated greatest improvement of solubility appropriate for rapid drug release, while membrane-coated beads appeared to have the greatest potential for sustained release and thereby the least possibility of precipitation during dissolution. These results suggest that appropriate dosage form design of CRASD systems is of potential to reduce the problem of precipitation during dissolution of poorly soluble drugs.