- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
04. October 2018
n recent years there has been a growing interest in solid lipid-based systems, particularly in solid lipid microparticles (SLMs); however, only very few studies deeply investigated the dissolution behaviour of orally delivered-SLMs. The present study provides new insights about the release performance in different gastrointestinal fluids of SLMs containing a freely water soluble drug (caffeine, as BCS class I drug). Three different formulations of SLMs were prepared by spray congealing using...
01. October 2018
The controlled release of caffeine from the casein gel tablets has been achieved over release periods lasting from a few minutes to over a few days. A novel casein gel has been acidified at pH of 1.0 as the insoluble controlled-release matrix and spray-dried with coffee for microencapsulation. The optimal inlet temperature of spray drying for the casein-coffee mixtures has been found to be 150 °C. The elastic casein-coffee tablets have been engineered without denaturing the components (as...
22. September 2018
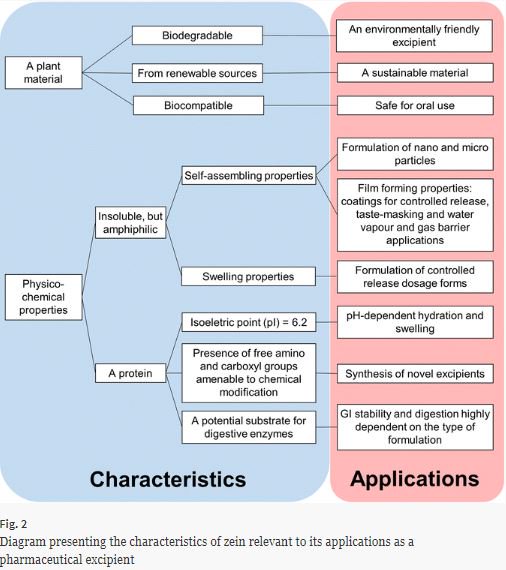
Zein is the main storage protein of corn and it has several industrial applications. Mainly in the last 10–15 years, zein has emerged as a potential pharmaceutical excipient with unique features. Zein is a natural, biocompatible and biodegradable material produced from renewable sources. It is insoluble, yet due to its amphiphilic nature, it has self-assembling properties, which have been exploited for the formation of micromicroparticle and nanoparticle and films. Moreover, zein can hydrate...
13. September 2018
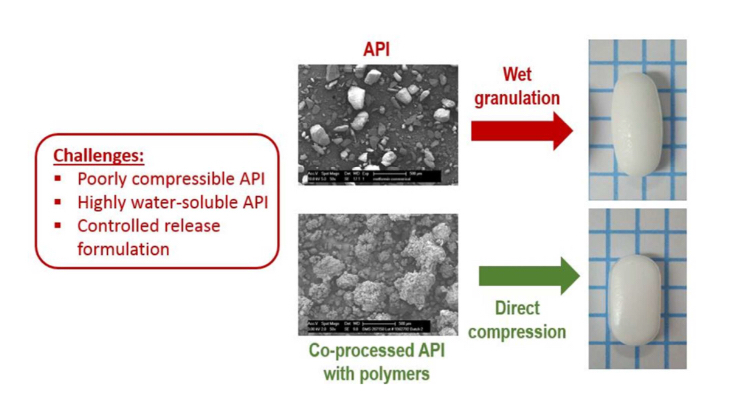
Herein we introduce an innovative process for preparation of directly compressible API and excipient agglomerates for extended release formulation of a highly water soluble drug, demonstrated with metformin HCl. Metformin is poorly compressible and currently employs wet granulation for tablet manufacturing, resulting in long cycle times. We have co-processed metformin HCl with hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and sodium carboxymethlycellulose (NaCMC) in solvent medium to generate...
12. September 2018
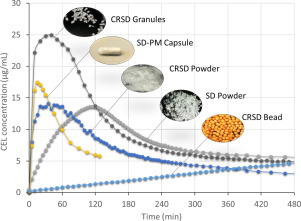
The amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) technique has been employed to formulate poorly-soluble drugs, however, development of solid dosage forms with ASD is challenging due to the high propensity of amorphous drug to precipitate upon dissolution. Thus this work aimed to explore the potential of controlled release amorphous solid dispersion (CRASD) systems using polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) as a release-retarding excipient to mitigate the drug precipitation during dissolution of poorly water-soluble...
26. May 2018
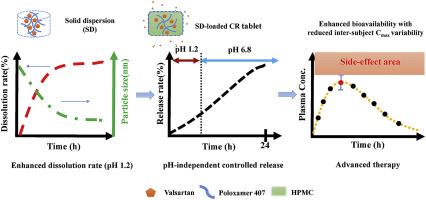
The aims of this work were to design pH-independent controlled release (CR) tablet containing nanonizing solid dispersion (SD) adsorbed on hydrophilic silica (Aeroperl® 300/30). Valsartan (VAL) was chosen to simultaneously modulate solubility and release rate due to its poor water solubility in low pH condition and short elimination half-life. Based on extensive equilibrium solubility and compatibility studies, poloxamer 407 was selected as a SD carrier. The melted mixtures of drug and...
15. May 2018
Zein is the main storage protein of corn and it has several industrial applications. Mainly in the last 10–15 years, zein has emerged as a potential pharmaceutical excipient with unique features. Zein is a natural, biocompatible and biodegradable material produced from renewable sources. It is insoluble, yet due to its amphiphilic nature, it has self-assembling properties, which have been exploited for the formation of micromicroparticle and nanoparticle and films. Moreover, zein can hydrate...
14. December 2017
Spatial and temporal control of drug delivery is of prime importance for establishing the therapeutic compliance of drugs for various diseases. Conventional approaches to drug delivery for temporal control of drug delivery include encapsulation, entrapment and conjugation to polymeric materials for obtaining the controlled release. Several macro, micro and nanoformulations have been researched and commercialized for producing controlled release of drugs. Apart from the control over the rate of...
13. October 2017
Osmotic pump delivery systems have made significant advances in the past decades for controlled drug release over a long period of time. Usually, osmotic pump products require sophisticated and expensive laser drill technology resulting in increase in production cost and decrease in production efficiency. In this study, a lamotrigine extended release tablet based on a controlled-porosity osmotic pump (CPOP) system was developed to circumvent laser drill technology in reference, Lamictal XR®....
28. September 2017
A comprehensive model with all effective phenomena in drug release such as diffusion, swelling and erosion was considered. In this work, a mathematical model was developed to describe drug release from controlled release HPMC matrices as a favorable system in pharmaceutical industries. As a novel study, the impact of the MCC presence as a filler in tablet preparation process was considered in the mathematical model. In addition, we found that the volume expansion of these polymeric matrices did...