- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
04. October 2018
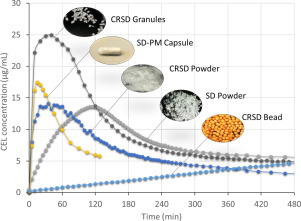
The aim of this work was to develop an ascending controlled-release pellet (ACRP) of paliperidone to improve poor solubility and provide a stable blood drug concentration. The inner core was produced by mixing different ratios of sodium chloride as an osmotic substance and microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) to offer a pressure drive when in contact with medium. After, the drug layer was processed by a liquid-layering method, with paliperidone ground to a nano-size in order to improve the...
04. October 2018
n recent years there has been a growing interest in solid lipid-based systems, particularly in solid lipid microparticles (SLMs); however, only very few studies deeply investigated the dissolution behaviour of orally delivered-SLMs. The present study provides new insights about the release performance in different gastrointestinal fluids of SLMs containing a freely water soluble drug (caffeine, as BCS class I drug). Three different formulations of SLMs were prepared by spray congealing using...
01. October 2018
The controlled release of caffeine from the casein gel tablets has been achieved over release periods lasting from a few minutes to over a few days. A novel casein gel has been acidified at pH of 1.0 as the insoluble controlled-release matrix and spray-dried with coffee for microencapsulation. The optimal inlet temperature of spray drying for the casein-coffee mixtures has been found to be 150 °C. The elastic casein-coffee tablets have been engineered without denaturing the components (as...
22. September 2018
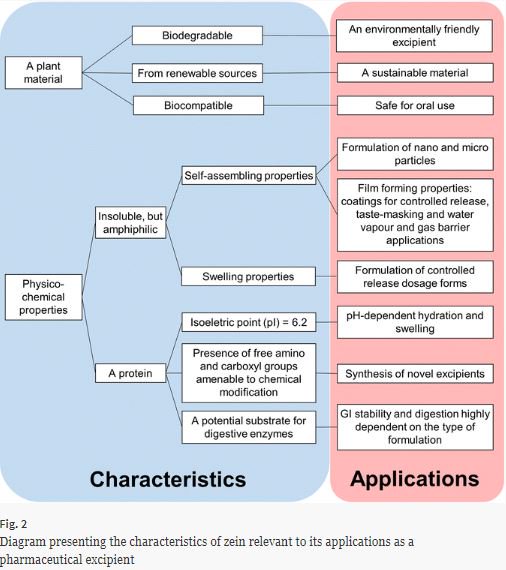
Zein is the main storage protein of corn and it has several industrial applications. Mainly in the last 10–15 years, zein has emerged as a potential pharmaceutical excipient with unique features. Zein is a natural, biocompatible and biodegradable material produced from renewable sources. It is insoluble, yet due to its amphiphilic nature, it has self-assembling properties, which have been exploited for the formation of micromicroparticle and nanoparticle and films. Moreover, zein can hydrate...
13. September 2018
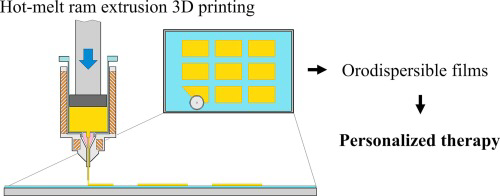
This work demonstrates the feasibility of the extemporaneous preparation of maltodextrins orodispersible films (ODF) by hot-melt ram-extrusion 3D printing. This method consists of three simple technological operations which can be also implemented in a pharmacy setting. First, maltodextrins, drug, and other excipients are mixed in a mortar and wetted with the plasticizer (i.e. glycerine). Then, the mixture is fed in the chamber of the ram-extruder and heated. ODF are individually printed on the...
13. September 2018
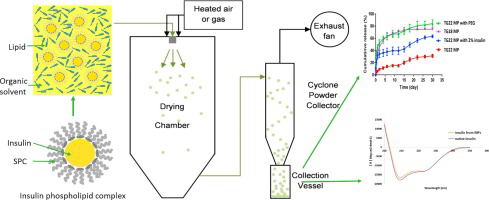
The study aimed at investigating the potential of spray drying method for encapsulation of protein drugs into solid lipid microparticles (MP) and evaluating effects of excipients on encapsulation and release of protein from MP. After transformation of model protein insulin to insulin-phospholipid complex, it was dissolved together with lipid excipients in organic solvent, which was spray-dried to form solid lipid MP. Polymeric MP with D, L-lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) were prepared similarly....
13. September 2018
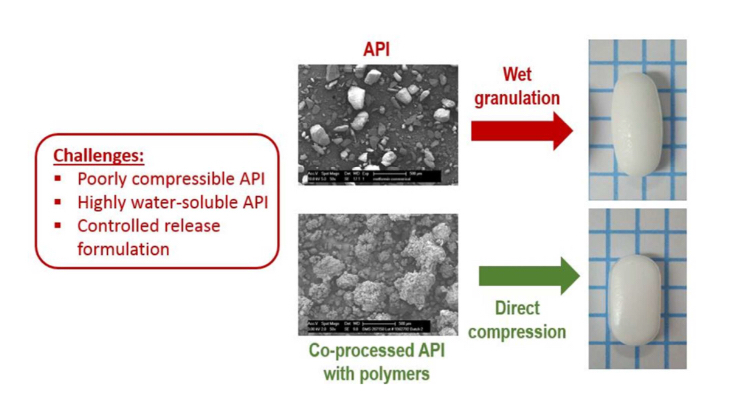
Herein we introduce an innovative process for preparation of directly compressible API and excipient agglomerates for extended release formulation of a highly water soluble drug, demonstrated with metformin HCl. Metformin is poorly compressible and currently employs wet granulation for tablet manufacturing, resulting in long cycle times. We have co-processed metformin HCl with hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and sodium carboxymethlycellulose (NaCMC) in solvent medium to generate...
12. September 2018
The amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) technique has been employed to formulate poorly-soluble drugs, however, development of solid dosage forms with ASD is challenging due to the high propensity of amorphous drug to precipitate upon dissolution. Thus this work aimed to explore the potential of controlled release amorphous solid dispersion (CRASD) systems using polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) as a release-retarding excipient to mitigate the drug precipitation during dissolution of poorly water-soluble...
04. September 2018
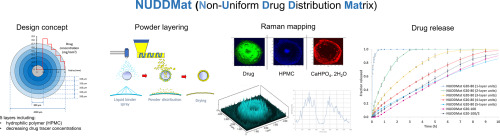
A decrease in the release rate over time is typically encountered when dealing with hydrophilic matrix systems for oral prolonged release due to progressive increase of the distance the drugmolecules have to cover to diffuse outwards and reduction of the area of the glassy matrix at the swelling front. In order to solve this issue, a novel formulation approach based on non-uniformdistribution of the active ingredient throughout the swellable polymer matrix was proposed and evaluated. Various...
02. September 2018
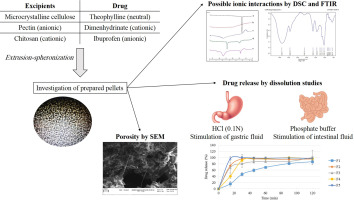
This study aimed to evaluate the potential of applying pectin and chitosan polysaccharides in pellet formulation. These biopolymers have advantages such as biocompatibility, low toxicity, low price and easy processing which make them interesting candidates for drug delivery purposes. Careful control of pellet porosity is essential to achieve an appropriate drug release profile. Replacing microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) with polysaccharides, especially pectin, leads to increased pellet...