- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
04. October 2018
Praziquantel is an antiparasitic drug used for decades. Currently, the praziquantel commercial preparation is a racemic mixture, inwhich only the levo-enantiomer possesses anthelmintic activity. The knowledge of its properties in the solid state and other chemical-physical properties is necessary for improving its efficacy andapplications. Drug solid dispersions were prepared with calcium carbonate at 1:5 drug to excipient weight ratio by solventevaporation method. Then, the modification of the...
04. October 2018
n recent years there has been a growing interest in solid lipid-based systems, particularly in solid lipid microparticles (SLMs); however, only very few studies deeply investigated the dissolution behaviour of orally delivered-SLMs. The present study provides new insights about the release performance in different gastrointestinal fluids of SLMs containing a freely water soluble drug (caffeine, as BCS class I drug). Three different formulations of SLMs were prepared by spray congealing using...
02. October 2018
The formulation of amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs) is an effective way to improve the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The combination of an amorphous state of the drug and the presence of crystallization-inhibiting polymers retains a high amount of dissolved API over time. ASDs with ketoconazole and different polymers were manufactured by spray drying and their characteristics as well as performance were analyzed. Dissolution tests with a...
15. September 2018
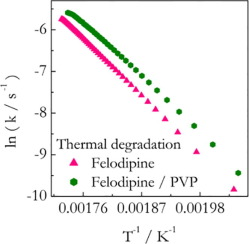
The present study explores the hypothesis that a polymer can affect the thermal stability of a drug in solid polymer-drug dispersions. The hypothesis is tested in a systematic fashion by combining isoconversional kinetic analysis with thermogravimetric measurements on several solid dispersions. Experimental systems involve three drugs: indomethacin (IMC), felodipine (FD), and nifedipine (ND) and their solid dispersions with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP). It is found that PVP stabilizes IMC but...
13. September 2018
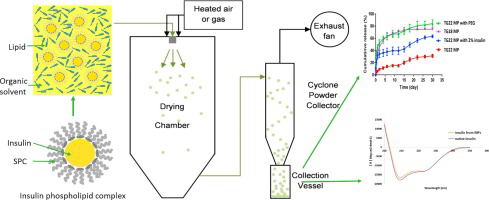
The study aimed at investigating the potential of spray drying method for encapsulation of protein drugs into solid lipid microparticles (MP) and evaluating effects of excipients on encapsulation and release of protein from MP. After transformation of model protein insulin to insulin-phospholipid complex, it was dissolved together with lipid excipients in organic solvent, which was spray-dried to form solid lipid MP. Polymeric MP with D, L-lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) were prepared similarly....
12. September 2018
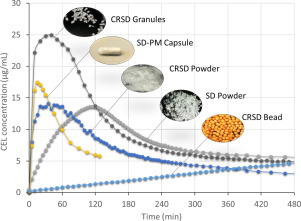
The amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) technique has been employed to formulate poorly-soluble drugs, however, development of solid dosage forms with ASD is challenging due to the high propensity of amorphous drug to precipitate upon dissolution. Thus this work aimed to explore the potential of controlled release amorphous solid dispersion (CRASD) systems using polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) as a release-retarding excipient to mitigate the drug precipitation during dissolution of poorly water-soluble...
05. September 2018
The predictability of preformulation screening tools for polymer selection in amorphous solid dispersions (ASD) regarding supersaturation and precipitation was systematically examined. The API-polymer combinations were scaled up by means of hot-melt extrusion and spray-drying to verify the predictions. As there were discrepancies between a solvent-based screening and performance of ASD, a new screening tool with improved predictability at minimal investments of time and material is presented....
30. August 2018
Hard gelatin capsule (HGC) shells are widely used to encapsulate drugs for oral delivery, but are vulnerable to gelatin cross-linking, which can lead to slower and more variable in vitro dissolution rates. Adding proteolytic enzymes to the dissolution medium can attenuate these problems, but this complicates dissolution testing and is only permitted by some regulatory authorities. Here, we expand the scope of our previous work to demonstrate that canisters containing activated carbon (AC) or...
30. August 2018
This study aimed to improve dissolution rate of valsartan in an acidic environment and consequently its oral bioavailability by solid dispersion formulation. Valsartan was selected as a model drug due to its low oral bioavailability (~23%) caused by poor solubility of this drug in the low pH region of gastrointestinal tract (GIT) and presence of absorption window in the upper part of GIT. Solid dispersions were prepared by solvent evaporation method with Eudragit® E100, Soluplus® or...
25. August 2018
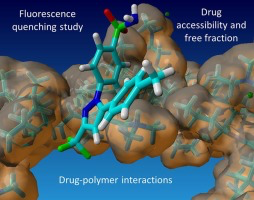
Solid dispersions (SDs) represent an important formulation technique to achieve supersaturation in gastro-intestinal fluids and to enhance absorption of poorly water-soluble drugs. Extensive research was leading to a rather good understanding of SDs in the dry state, whereas the complex interactions in aqueous medium are still challenging to analyze. This paper introduces a fluorescence quenching approach together with size-exclusion chromatography to study drug and polymer interactions that...