Abstract
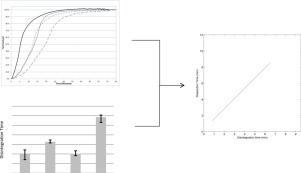
The drug release rate of a rapidly dissolving immediate-release tablet formulation with a highly soluble drug is proposed to be controlled by the disintegration rate of the tablet. Disintegration and dissolution test methods used to evaluate the tablets were shown to discriminate manufacturing process differences and compositionally variant tablets. In addition, a correlation was established between disintegration and dissolution. In accordance with ICH Q6A, this work demonstrates that disintegration in lieu of dissolution is suitable as the drug product quality control method for evaluating this drug product.
Conclusion
A discriminating dissolution method was developed for two strengths of an immediate-release, highly soluble drug product. The high solubility of the drug along with the observation of rapidly dissolving immediate-release tablets suggests that the drug release from the dosage form is limited by disintegration. A linear relationship was demonstrated between disintegration and dissolution results for the drug product. Disintegration testing using USP <701> is therefore an appropriate drug product quality control method for evaluating drug release from this dosage form.