- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
31. March 2018
The growing popularity of direct-compression process necessitates an ideal filler–binder that can substitute two or more excipients. Pregelatinization of starches significantly improves swelling and flow properties but produces tablets with low mechanical strength.
17. February 2018
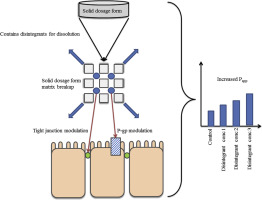
Abstract Pharmaceutical excipients were designed originally to be pharmacologically inert. However, certain excipients were found to have altering effects on drug pharmacodynamics and/or pharmacokinetics. Pharmacokinetic interactions may be caused by modulation of efflux transporter proteins, intercellular tight junctions and/or metabolic enzyme amongst others. In this study, five disintegrants from different chemical classes were evaluated for P-glycoprotein (P-gp) related inhibition and tight...
13. February 2018
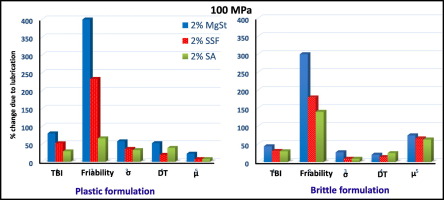
As an essential formulation component for large-scale tablet manufacturing, the lubricant preserves tooling by reducing die-wall friction. Unfortunately, lubrication also often results in adverse effects on tablet characteristics, such as prolonged disintegration, slowed dissolution, and reduced mechanical strength.
12. February 2018
There is considerable interest in formulations with high active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) load, for reasons including lower patient tablet burden and therefore, potentially improved patient adherence. This remains a challenge not least because most APIs are poor flowing.
30. December 2017
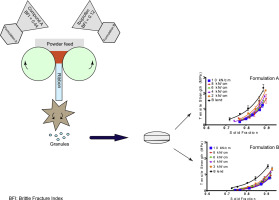
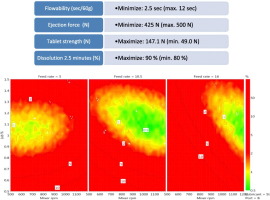
The objective of this study was to devise robust and stable continuous manufacturing process settings, by exploring the design space after an investigation of the lubrication-based parameters influencing the continuous direct compression tableting of high dose paracetamol tablets.
18. December 2017
The drug release rate of a rapidly dissolving immediate-release tablet formulation with a highly soluble drug is proposed to be controlled by the disintegration rate of the tablet. Disintegration and dissolution test methods used to evaluate the tablets were shown to discriminate manufacturing process differences and compositionally variant tablets.
25. November 2017
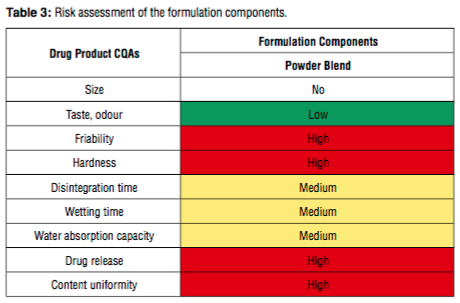
In this study, within the framework of Quality by Design which is a systemati- cally scientific approach which enables to understand and control the production and formulation variables during the process design and development, different parameters in the formulation and production process were detected and criti- cal process parameters and critical material attributes were determined via risk evaluation methods. Then, different oral disintegrating tablet formulations were prepared and tested b
17. October 2017
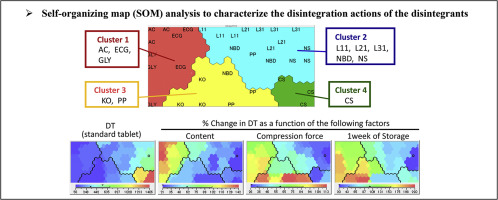
To gain a better understanding of disintegration actions, 11 different disintegrants were tested. Model tablets were prepared with various preparation conditions, and their disintegration time and tensile strength were measured.