- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
31. December 2017
The FDA clarified the regulatory thicket surrounding the 505(b)(2) approval pathway for drug formulations just over a decade ago. In the intervening years, this pathway has become an increasingly popular way for drug makers to commercialize products. The 505(b)(2) pathway allows companies to make modest changes to an already approved drug and get continued market exclusivity for from three to as many as seven years.
30. December 2017
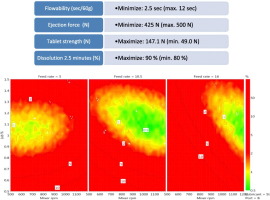
The objective of this study was to devise robust and stable continuous manufacturing process settings, by exploring the design space after an investigation of the lubrication-based parameters influencing the continuous direct compression tableting of high dose paracetamol tablets.
30. December 2017
Among the strategies to improve the biopharmaceutic properties of poorly soluble drugs, Supersaturating Drug Delivery Systems like polymer-based amorphous solid dispersions (SD) have been successfully applied. The screening of appropriate polymeric carriers to compose SD is a crucial point on their development.
27. December 2017
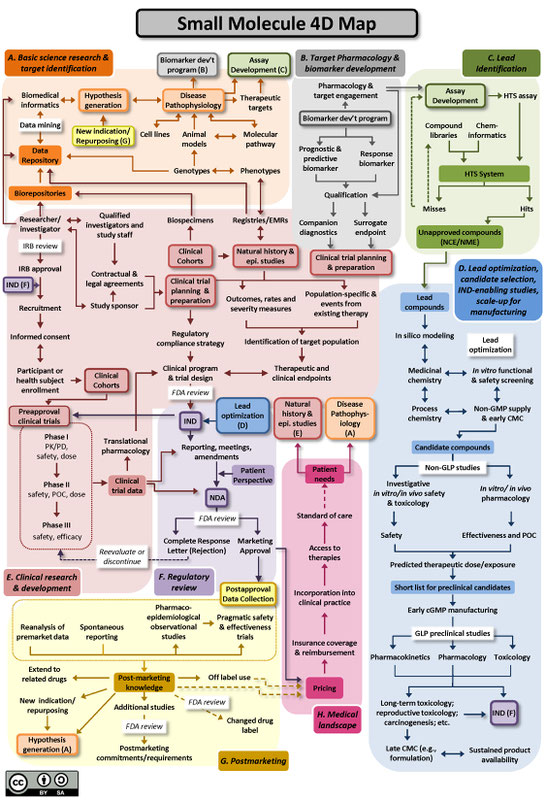
The Drug Discovery, Development and Deployment Maps (4DM) provide dynamic representations of the modern therapeutic development process to more easily identify inefficiencies and integrate efforts to expedite new therapies for patients. The maps provide a common framework for discussing the therapeutic development process and serve as an education tool for those who are new to it.
27. December 2017
Fun IMCD US Pharma Holiday Card 2017 - Featuring THE EXCIPIENTEERS and their Super Powers!
27. December 2017
The aim of this study was to develop a solid dosage form for pediatric application. For this purpose, hyaluronic acid was covalently linked with sulfhydryl groups of cysteine ethyl ester via amide bond formation mediated by carbodiimide.
26. December 2017
Micro sponge is a novel approach for targeting the drug to the colon for the management of colon ailments such as inflammatory bowel disease. Prednisolone loaded microsponges (PLMs) were prepared and coated with Eudragit S 100 (ES) and evaluated for colon specific drug delivery.
26. December 2017
This study presents an interesting and promising strategy for producing an oral multiparticulate formulation of the sustained-release of diclofenac sodium (DS) consisting of subunits closed inside hard gelatin capsules (each capsule contains ~ 50 mg of diclofenac sodium). The subunits in the form of beads were produced through the encapsulation of diclofenac sodium dispersed within a nondisintegrating polymer carrier by a silica gel functionalized with the 3-aminopropyl groups.
26. December 2017
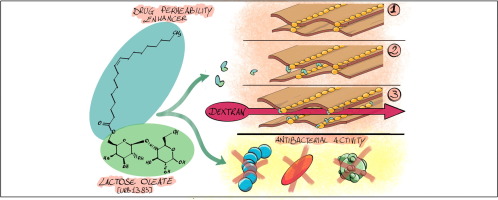
Sugar fatty acid esters are an interesting class of non-ionic, biocompatible and biodegradable sugar-based surfactants, recently emerged as a valid alternative to the traditional commonly employed (e.g. polysorbates and polyethylene glycol derivatives). By varying the polar head (carbohydrate moiety) and the hydrophobic tail (fatty acid), surfactants with different physicochemical characteristics can be easily prepared.
25. December 2017
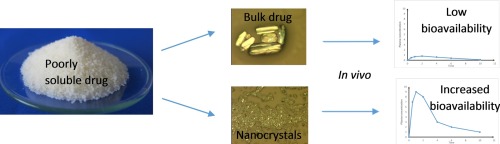
Poor solubility of drug compounds is a great issue in drug industry today and decreasing particle size is one efficient and simple way to overcome this challenge. Drug nanocrystals are solid nanosized drug particles, which are covered by a stabilizer layer.