Hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) is a water-soluble polymer used as a binder during pharmaceutical tableting and granulation. HPC is also known as a base material for pharmaceutical film by virtue of its film formability with excellent plasticity.
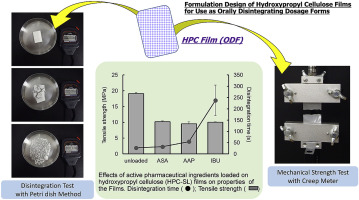
The aim of this study was to assess the applicability of HPC to orally disintegrating film (ODF) and to investigate optimization of the ODF formulation of HPC. The effects of the molecular weight of HPC and the addition of active pharmaceutical ingredients and excipients on the properties of ODFs prepared using HPC were evaluated. The results showed that a suitable grade of HPC as a base material for ODFs should be used in a suitable concentration in solution. The results also clarified that the disintegration time markedly decreased as the thickness of HPC films decreased. These properties could be controlled by adjusting the ingredients added to the formulation. While loading the film with ibuprofen prolonged the disintegration time, adding calcium carbonate particles to the film shortened it. These results demonstrated that HPC can be used as a base material for ODF applications.