Abstract
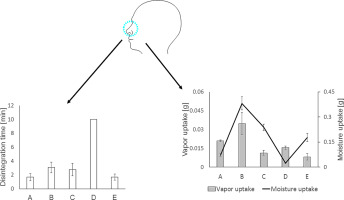
This present study intended to provide nasal adhesive formulations for the topical treatment of dry nasal syndrome. Mucoadhesive films were prepared according to solvent evaporation method consisting of well-known polymers such as gellan and carboxymethyl cellulose. Mucoadhesive films (A–E) were evaluated in respect to their physicochemical properties, stability, disintegration behavior and tensile strength. Moreover, uptake capacity of adhesive films was investigated according to three assays vapor uptake/ permeability and water uptake. Mucoadhesive assessment was carried out on porcine nasal mucosa in terms of adhesion time, wash off resistance and spreadability. Obtained finings indicated 4.2 (B) > 2.55 (A) > 1.8 (D) > 1.3 (C) > 1(E) fold vapor uptake ranking. The bioadhesive results indicated a 60-fold (B) > 8.58-fold (C) > 7.42-fold (E) > 1.3-fold (D) improvement in comparison to formulation A. A variety of humectants such as urea, Aloe vera, allantoin and hyaluronic acid was incorporated in the formulations. Taken together, nasal adhesive films convinced with their proficiency of mucoadhesiveness and stability to be suitable in the management of dry nasal syndrome.
Conclusion
Within this present work, a solid dosage form was developed for nasal application.
These solid dosage forms were observed for in situ gelling properties and mucoadhesiveness on the nasal mucosa. The composition of adhesive films with the combination of various humectants such as allantoin, urea, hyaluronic acid, provided lubrication in cases of mucosal dryness. Taken together, all five formulation showed promising results in mucoadhesion and mucoprotection. Further, F (B) containing aloe vera seemed the most auspicious one in terms of therapeutic potential for nasal impairment. The solid dosage forms were easy and convenient to apply rendering to high patients ́ compliance. The mucoadhesive films lead to less frequent applications and high acceptance in the nasal delivery.
Recommended for you