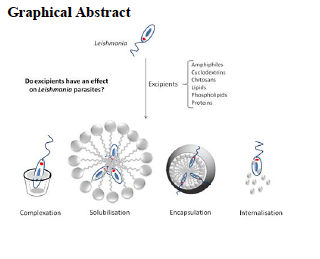
Leishmaniasis is a neglected tropical disease responsible for the ninth largest disease burden in the world threatening 350 million people mostly in developing countries. The lack of efficacy, severe adverse effects, long duration, high cost and parenteral administration of the current therapies result in poor patient compliance and emergence of resistance. Leishmaniasis' unmet need for safer, affordable and more effective treatments is only partly addressed by today's global health product pipeline that focuses on products amenable to rapid clinical development, mainly by reformulating or repurposing existing drugs for new uses. Excipients are necessary for ensuring the stability and bioavailability of currently available antileishmaniasis drugs which in their majority are poorly soluble or have severe side-effects. Thus, selection of excipients that can ensure bioavailability and safety as well as elicit a synergistic effect against the Leishmania parasites without compromising safety will result in a more efficacious, safe and fast to market medicine. We have evaluated the in vitro activity of 30 commercially available generally regarded as safe (GRAS) excipients against different Leishmania spp., their cytotoxicity and potential use for inclusion in novel formulations. Amongst the tested excipients, the compounds with higher selectivity index were Eudragit E100 (cationic triblock copolymer of dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate, butyl methacrylate, and methyl methacrylate), CTAB (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, cationic), lauric acid, Labrasol(non-ionic, caprylocaproyl polyoxyl- 8 glycerides) and sodium deoxycholate. An ideal excipient need to possess amphiphilic nature with ionic/polar groups and possess a short or medium fatty acid chain such as lauric (C12), capric C10) or caprylicacid (C8). Inclusion of these excipients and identification of the optimal combination of drug and excipients would lead to a more effective and safer antileishmanial therapies.
- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact