Abstract
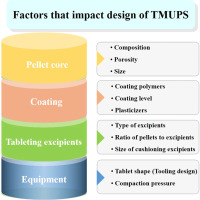
The tablet of multi-unit pellet system (TMUPS), using coated pellets, for controlled release of drugs is an effective therapeutic alternative to conventional immediate-release dosage forms. The main advantages of TMUPS include a) ease of swallowing and b) divisible without compromising the drug release characteristics of the individual units. TMUPS can be prepared more economically than pellet-filled capsules because of the much higher production rate of tableting process. In spite of the superiorities of TMUPS, its adoption has been challenged by manufacturing problems, such as compromised integrity of coated pellets and poor content uniformity. Herein, we provide an updated review on research, from both scientific literatures and patents, related to the compaction of TMUPS. Factors important for the successful production of TMUPS are summarized, including model drug property, potential cushioning agents, and novel techniques to protect pellets from damage. This review is intended to facilitate the future development of manufacturable TMUPS with drug release behavior similar to that of the original coated pellets.