- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
04. October 2018
n recent years there has been a growing interest in solid lipid-based systems, particularly in solid lipid microparticles (SLMs); however, only very few studies deeply investigated the dissolution behaviour of orally delivered-SLMs. The present study provides new insights about the release performance in different gastrointestinal fluids of SLMs containing a freely water soluble drug (caffeine, as BCS class I drug). Three different formulations of SLMs were prepared by spray congealing using...
15. September 2018
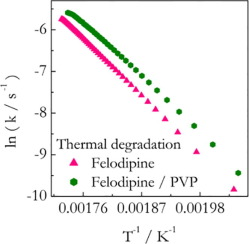
The present study explores the hypothesis that a polymer can affect the thermal stability of a drug in solid polymer-drug dispersions. The hypothesis is tested in a systematic fashion by combining isoconversional kinetic analysis with thermogravimetric measurements on several solid dispersions. Experimental systems involve three drugs: indomethacin (IMC), felodipine (FD), and nifedipine (ND) and their solid dispersions with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP). It is found that PVP stabilizes IMC but...
31. August 2017
Systematic Design of Experiment (DoE) approach.
Simultaneous analysis of the effect of process and formulation factors.
Studying molecular level interactions via FTIR and SSNMR analyses.
04. April 2017
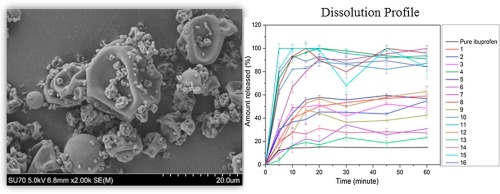
Abstract Ibuprofen is an oral analgesic usually processed by wet granulation. In this manuscript a new roller compaction process for ibuprofen is reported. The low melting point of ibuprofen is a critical point to be considered during processing. Melting of ibuprofen and its posterior solidification leads to a lower soluble form. The hypothesis of this work is that crystallinity of ibuprofen may be a good indicator of the quality for both raw material selection and the granules obtained during...
24. March 2017
Abstract Recent work established polymer strip films as a robust platform for delivery of poorly water-soluble drug particles. However, a simple means of manipulating rate of drug release from films with minimal impact on film mechanical properties has yet to be demonstrated. This study explores the impact of film-forming polymer molecular weight (MW) and concentration on properties of polymer films loaded with poorly water-soluble drug nanoparticles. Nanoparticles of griseofulvin, a model...
27. February 2017
Abstract Micronized cocrystal powders and amorphous spray-dried formulations were prepared and evaluated in vivo and in vitro as pulmonary absorption enhancement formulations of poorly soluble itraconazole (ITZ). ITZ cocrystals with succinic acid (SA) or l-tartaric acid (TA) with a particle size diameter of <2 μm were successfully micronized using the jet-milling system. The cocrystal crystalline morphologies observed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) suggested particle shapes that...
18. January 2017
Abstract Objectives: The work objective was to study the possible effects of different pharmaceutical excipients on the release of sodium salicylate from oily vehicles. Methods: Several formulations of Fractionated Coconut Oil (FCO) containing different pharmaceutical additives were prepared. The release rate behaviour of sodium salicylate from these oily formulations was investigated using a dialysis method. The time required for 30% and 50% of the salicylate to appear in solution outside the...
21. December 2016
Abstract Synergetic role of polymer blending on dissolution of amorphous solid dispersion was investigated. Dissolution rates of hypromellose (HPMC) and methacrylic acid copolymer (EUD) from the HPMC/EUD spray-dried sample (SPD) were improved compared to those of each single polymer SPD. Differential scanning calorimetry measurements revealed that the structural change in HPMC following heating was inhibited by co-spray-drying with EUD, suggesting an intermolecular interaction between the...
11. October 2016
Abstract One of the main obstacles to the successful treatment of tuberculosis is the poor and variable oral bioavailability of rifampicin (RIF), which is mainly due to its low hydrophilicity and dissolution rate. The aim of this work was to obtain a hydrophilic new material that allows a very fast dissolution rate of RIF and therefore is potentially useful in the development of oral solid dosage forms. The acid form of carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) was co-processed with RIF by solvent...
30. September 2016
ABSTRACT Oral dosage form is the physical form of a dose of a chemical compound used as a drug or medication intended for administration or consumption by the oral route. The poor dissolution rate of water insoluble drugs is still a substantial problem confronting the pharmaceutical industry. There are several methods used to increase the solubility of drugs, of those liquid-solid compact (LSC) technique is a new and promising addition towards such a novel aim, that the solubility of the...