- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact
04. October 2018
n recent years there has been a growing interest in solid lipid-based systems, particularly in solid lipid microparticles (SLMs); however, only very few studies deeply investigated the dissolution behaviour of orally delivered-SLMs. The present study provides new insights about the release performance in different gastrointestinal fluids of SLMs containing a freely water soluble drug (caffeine, as BCS class I drug). Three different formulations of SLMs were prepared by spray congealing using...
22. September 2018
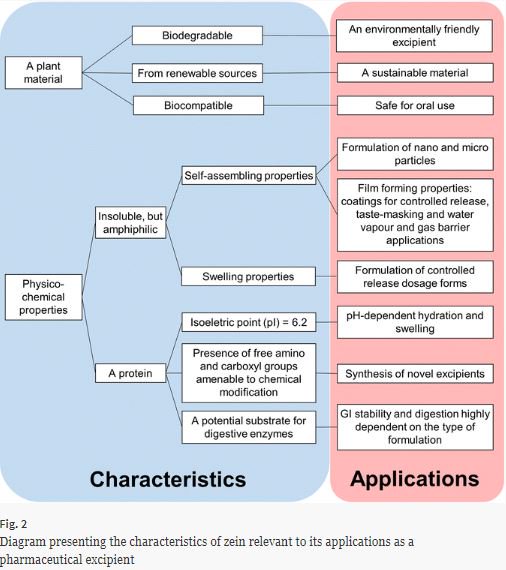
Zein is the main storage protein of corn and it has several industrial applications. Mainly in the last 10–15 years, zein has emerged as a potential pharmaceutical excipient with unique features. Zein is a natural, biocompatible and biodegradable material produced from renewable sources. It is insoluble, yet due to its amphiphilic nature, it has self-assembling properties, which have been exploited for the formation of micromicroparticle and nanoparticle and films. Moreover, zein can hydrate...
15. September 2018
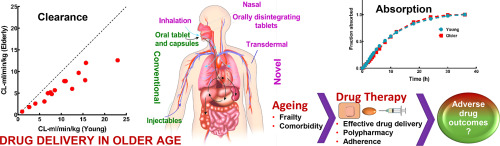
Both drug delivery performance and various age-related physical, mental and physiological changes can affect their effectiveness and safety in elderly patients. The many drug delivery systems developed over the years include recent novel transdermal, nasal, pulmonary and orally disintegrating tablet delivery systems that provide consistent, precise, timely and more targeted absorption. Certain drug delivery systems may be associated with suboptimal outcomes in the elderly because of the nature...
04. September 2018
Diabetes mellitus is a highly prevalent metabolic and chronic disease affecting millions of people in the world. The most common route of insulintherapy is the subcutaneous injection due to its low bioavailability and enzymatic degradation. The search for effective and high patient compliance insulin delivery systems has been a major challenge over many decades. The polysaccharide-based nanoparticles as delivery vehicles for insulin oral administration have recently attracted substantial...
30. August 2018
Hard gelatin capsule (HGC) shells are widely used to encapsulate drugs for oral delivery, but are vulnerable to gelatin cross-linking, which can lead to slower and more variable in vitro dissolution rates. Adding proteolytic enzymes to the dissolution medium can attenuate these problems, but this complicates dissolution testing and is only permitted by some regulatory authorities. Here, we expand the scope of our previous work to demonstrate that canisters containing activated carbon (AC) or...
26. August 2018
The aim of this study was to develop roflumilast dry powder inhaler (DPI) formulations by spray drying using hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβCD) and to determine their suitability for pulmonary delivery. Different feed solution concentrations, solvent systems and spray drying parameters were used to obtain the formulations which were characterized using X-ray powder diffraction, thermal analysis, scanning electron microscopy, particle size distribution, bulk and tapped density, specific...
25. August 2018
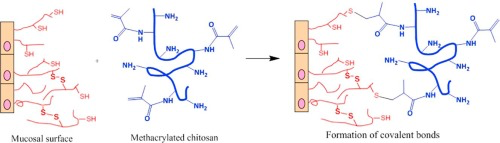
Chitosan is a cationic polysaccharide that exhibits mucoadhesive properties which allow it to adhere to mucosal tissues. In this work, we explored chemical modification of chitosan through its reaction with methacrylic anhydride to synthesise methacrylated derivative with the aim to improve its mucoadhesive properties. The reaction products were characterised using 1H NMR, FTIR and UV–Vis spectroscopy. 1H NMR and ninhydrin test were used to quantify the degree of methacrylation of chitosan....
25. August 2018
In recent years, excipient development has become a core area of research in pharmaceutical drug delivery because it influences the formulation development and drug delivery process in various ways. Polymeric drug delivery systems have been of great interest for controlled delivery as they show the great advantage in drug delivery systems because of optimized drug loading and releasing property. Then, the side effects of synthetic polymers far exceed that it leads to some difficulties like they...
18. August 2018
Older adults with multimorbidity, polypharmacy, and complex health needs are the major consumer of health care. Ensuring that medicines are used safely, effectively, and delivered efficiently in this population is challenging. In this context, the approach to medicines delivery should seek to overcome some of the difficulties of delivering medicines to older people, and ensure each medication is delivered by the optimal and most convenient route for the patient in question. However, this poses...
08. August 2018
Polymeric gels have emerged as promising vehicles for drug delivery across the skin. Stratum corneum, the topmost layer of the skin, does not allow hydrophilic and high molecular weight drugs to permeate without enhancing techniques. A number of enhancement techniques are being developed to increase the transdermal drug permeation. The transdermal route has many advantages and has therefore evolved as an attractive and convenient alternative to the existing routes of drug delivery that causes...