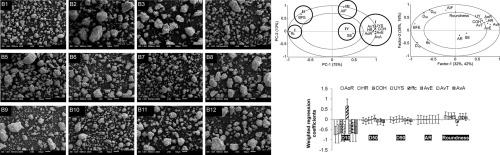
Powder flow is critical to the success of various pharmaceutical processes such as tableting and capsule filling. Despite a plethora of flow characterisation techniques and parameters available,
powder flow still remains to be a not well understood subject. Inter-relationships between the various powder flow parameters in particular have not been well established. Furthermore, while it is
known that particle size and shape are important determinants of powder flow, their relative impact on individual flow parameter is unclear. In this study, granules were evaluated for their flow
properties using various characterisation methods. Through multivariate analysis, flow parameters were classified based on the underlying physical granule property. Angle of repose, Hausner ratio,
shear cell parameters and avalanche flow were found to be affected primarily by powder cohesion, which was in turn determined by the smallest granule size fraction. On the other hand, powder
compressibility and inter-particulate friction were the main factors underlying basic flow energy. Angle of internal friction was primarily affected by particle roundness and did not appear to
describe powder bulk flow properties. This study showed that while the various flow characterisation techniques were different in terms of their applications, there were common physical attributes
that governed the measurements.
- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact