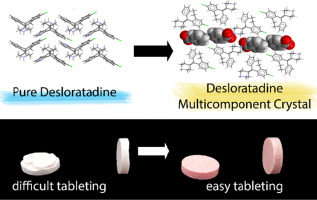
We report the first multicomponent crystal of desloratadine, an important anti-histamine drug, with a pharmaceutically acceptable coformer of benzoic acid. The single crystal structure analysis revealed that this novel multicomponent crystal is categorized as salt due to the proton transfer from benzoic acid to the desloratadine molecule. By forming the salt multicomponent crystal, we demonstrated that the tabletability and plasticity of the multicomponent crystal was improved from the parent drug. In addition, neither capping nor lamination tendency was observed in the desloratadine-benzoic acid multicomponent crystal. The existence of a layered structure and slip planes are proposed to be associated with this improvement. The desloratadine-benzoate in this case shows an improved solubility in water and HCl 0.1N media and a better dissolution profile in water. However, the dissolution rate in HCl 0.1N media was found to be essentially indifference.
- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact