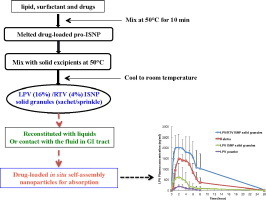
The aim of this study was to develop a nanotechnology to formulate a fixed-dose combination of poorly water-soluble drugs in a children-friendly, flexible solid dosage form. For diseases like HIV, pediatric patients are taking multiple drugs for effective treatments. Fixed-dose combinations could reduce pill burdens and costs as well as improving patient adherence. However, development of fixed-dose combinations of poorly water-soluble drugs for pediatric formulations is very challenging. We discovered a novel nanotechnology that produced in situ self-assembly nanoparticles (ISNPs) when the ISNP granules were introduced to water. In this study, antiretroviral drug granules, including lopinavir (LPV) ISNP granules and a fixed-dose combination of LPV/ritonavir (RTV) ISNP granules, were prepared using the ISNP nanotechnology, which spontaneously produced drug-loaded ISNPs in contact with water.
- Home
- Blog
- News
- Basics
- Sources
- Agencies, Regulatory & Organisations
- CERSI Excipients Browser
- Excipient Report
- Excipient DMF List
- EXCiPACT Certified Companies
- Excipient Documentation
- Excipient EINECS Numbers
- Excipient E-Numbers
- FDA Inactive Ingredient List
- FDA GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
- IPEC Americas
- USP - U.S. Pharmacopeia
- Definitions
- Whitepapers / Publications
- Supplier
- Services
- Media
- Events
- 1st pharmaexcipients Poster Award
- Event Calendar
- Events featured by pharma-excipients
- 4th Annual Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
- DDF Summit
- ExcipientFest Americas
- ExcipientFest Asia
- Global CompliancePanel
- International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutics & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Formulation & Drug Delivery USA Congress
- Laboratory Medicine 2018
- Making Pharmaceuticals Europe
- Making Pharmaceuticals Exhibition
- Pharma Integrates
- PharmaExcipients China @CPhI China
- TTC Technology Training Center
- Jobs
- Online Sourcing
- Contact